Aquaponics System Design: Learn step-by-step
Aquaponics is a type of agriculture that contains fish and plants in the same landscape where they can help each other or, in other words, symbiotically. It is a linked production method, employing aquaculture (the rearing of fish) and hydroponics (the plant growing in water), that gives rise to an autonomous and eco-friendly system. In this summary, we will cover and discuss the Aquaponics system design step-by-step: fundamentals of aquaponics, design ideas, and community involvement potential of urban aquaponic farming, the various types, and how a step-by-step brace is implemented.
What is Aquaponics? And how does it work?
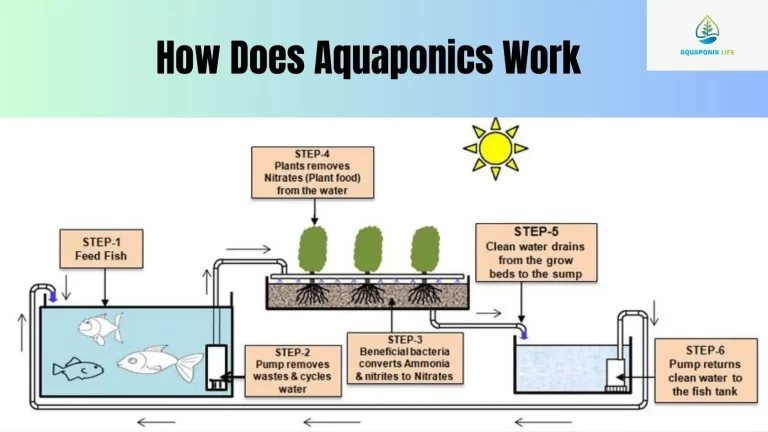
Aquaponics is a system combining aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics. Aquaponics is an imitation of outdoor natural water and nutrient cycle that usually happens in aquatic or marine ecosystems. It consists of three main components: trace elements such as calcium, magnesium, iron, iodine, selenium, zinc, and many other microbes.
To know more about What is Aquaponics, Read my article :
The fish are waste makers, and this waste is primarily rich in ammonia as well as other compounds. The bacteria use ammonia as a source of energy to produce nitrites and then further convert the nitrites into nitrates, which is essential for the plants to survive. The plants parasitically take the nitrogen compounds and other minerals from the water, while the fish proof the water with their wastes. It is recirculated through water channels directly to the fish tank in a closed-loop system, so it does not need much outside input or create waste of this kind.
Types of Aquaponics Systems
Three styles of aquaponic systems exist, which differ based on how water is distributed between the fish lake and the plant bed.
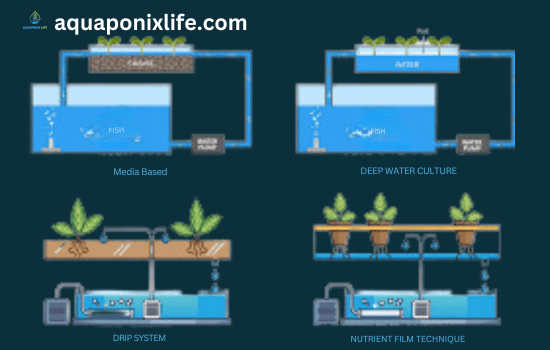
Nutrient Film Technique or NFT
In this case, the system uses a fragile film of water that goes downwards along pipes and channels, where the plant’s roots are placed inside the pipes but outside the channel.
This way of water is used to carry nutrients to the plants and then evaporates back to the fish tank. Such a system is well-suited to leafy and light-made plants of this group – for example, lettuce, basil, or mint.
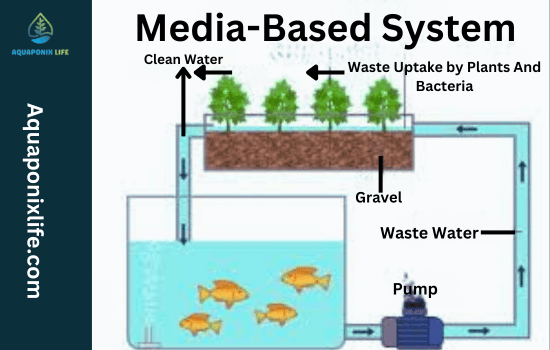
Media Bed or Grow bed
In this system (hydroponics), you have it so that the roots of the plants can be supported on a bed of solid media, either gravel, clay pebbles, or perlite.
The fish tank water irrigates the plants periodically, and the plants obtain nutrients and oxygen from the water through the media bed. Media, in this context, being a waste filter, traps solids and hosts the positive ones.
The hydroponic system is crucial in availing enough space for these plants like tomatoes, pepper, cucumber, and other larger and heavier crops.
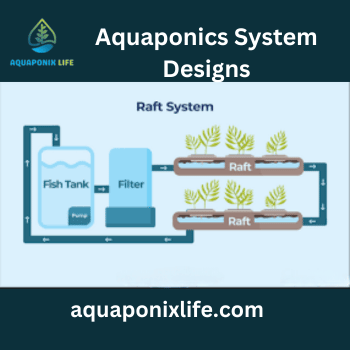
Deep Water Culture or Raft System
It operates on a reservoir or canal filled with water, while the individual plants are grown on rafts or net pots. This is done by using an aerator to deliver the elements through a pipe to the roots of the plants.
The water level is managed by a siphon or a standpipe, which does the in-between not exceeding part of the aquarium back to the fish tank. The stem system for these plants is ideal for quick-growing crops such as leafy greens, including kale, spinach, and chard.
Drip System:
A drip irrigation system is used in aquaponics to keep fish and plants in balance. Grow beds that are filled with a media such as expanded clay pellets, coco coir, or gravel are pounded with water from the fish tank. In order to guarantee that every plant gets the proper amount of moisture, the system properly distributes water and controls the flow. By doing this, water efficiency is increased and water loss is reduced.
Because helpful bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and nitrates, the drip system also makes it easier for plants to receive nutrients from fish waste. It makes it possible to precisely regulate watering levels and schedules, promoting healthy plant growth and averting soggy situations. In order to maximize crop yields and support the health of plants and fish, this system is essential.
Components of Aquaponics System
To understand How does aquaponics work , we need to address its components firstly.
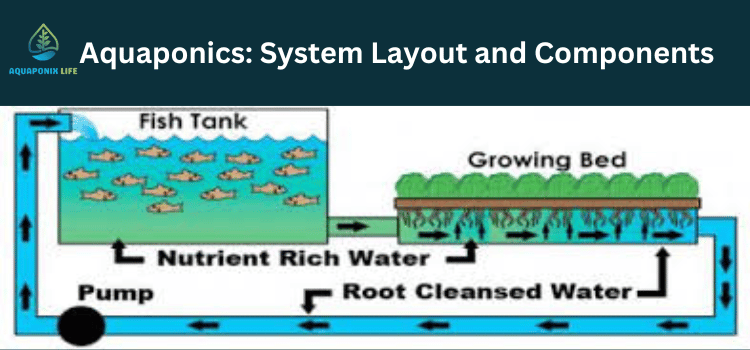
Fish Tank
The fish tank is the central part of the aquaponic system where the aquaculture component takes place.
It needs to be big enough for the fish to have enough room to live and contain a sorption system that periodically cleans the water.
Grow Beds
The grow bags are the boxes filled with the growing medium in which the plant is grown. This is where the plants’ roots will work to withdraw the nutrients from the fish waste that supply essential minerals and nutrients to the plant.
The design should take proper care of drainage and aeration to offer excellent growth for plants.
Water Pump
The pump destined to draw water from the fish tank to the grow beds is the most vital part of the hydroponic system. It provides water full of plant nutrients and is a purifying element for the fish.
Piping System
An appropriately designed sound piping system provides a smooth and efficient water flow between the aquarium and the planting troughs. Correct piping size and arrangement are needed to let the water flow freely and eliminate any possible blockage.
How To Build Easy and Cheap Aquaponics Design?
When building such systems, a few fundamental considerations need to be addressed. Installing aquaponic systems is a function of the following operations: size, site, budget, and purpose. However, some general steps can be followed to create a basic system:
Choose the Type of System
Review the available space and crop you would like to grow, and consider the system’s complexity degree to find the best purpose-built system for your situation. You can use the same system everywhere and create a combination of systems using a media bed as the central plants and NFT to hang the herbs.
Choose the Fish and Plants
Pick out the fish and plants that can live together and thrive under the environmental conditions of your new system. For instance, the choice of tilapia or catfish from the warm and cold water. You will have trout, perch, and salmon. You can also opt for plants with similar nutrient and pH needs, like lettuce, basil, and mint, or tomato, peppers, eggplant, etc.
Setting up the Materials and Equipment
Assemble materials and all the necessary equipment that you‘ll use to create your system. This requires tanks, pipes, pumps, filters, media, rafts, net pots, etc. You can also assemble your equipment using recycled items such as drums, buckets, or pallets to save money and reduce waste. You can, furthermore, engage in the endeavor of bringing some research materials into the picture.
Set up the Fish Tank
Put the different components of your system into use according to the design plan and the instructions. Check for leaks, pumps, and flow before introducing fish and other plants into the system. This can be repeated for a few weeks by the addition of such things as ammonia or fish food, which will balance the bacterial colony and water chemistry.
Pour the Fish and Harvest the Plants
For the cyclic life to thrive in your system, introduce fish and plants slowly and avoid stress and shock. Monitoring the water quality parameters includes temperature, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels and their respective adjustments per their needs. Again, feed the fish regularly, but watch not to overfeed and trim the plants as they grow. Get satisfied with the pleasure of collecting and preserving your produce when it is ready.
Elements Need when Developing an Aquaponics System
Water Quality
Water quality, which is essential to protect both fish and plants, can either be deadly or the reason for their growth and therefore, we must do our best to keep it at the maximum possible level at all times. The design should include sufficient filtration facilities, including solids filters and biofilters that will be used to remove waste and macronutrients from the water.
Lighting
One must ensure plants get enough light; this is for the process of photosynthesis. For example, the beds should be positioned near windows that receive sufficient sunlight; alternatively, if cultivated indoors, the system can be equipped with continuous and uniform artificial lighting for optimal productivity.
Temperature Control
Fish and plants are characterized by warm and cold habitats that favor their best growth. Considerations regarding water temperature should include approaches to regulate the water temperature, such as using heating means or cooling systems.
System Scalability
A scale-worthy design should permit upscaling to facilitate further growth or make improvements when production objectives change. Open structure modification in system design puts aquaponic farmers in a position to adjust their system as required.
Benefits of Using An Aquaponics System Design
Resource Efficiency
Aquaponics systems are water-efficient since the same water is continuously reused between the fish tank and grow beds, reducing water usage. The fish have essential nutrients, causing waste that is also being recycled. In the end, this minimizes the need for more fertilizers.
Space Utilization
With the adoption of aquaponics systems, they can be built on several scales to be conveniently used in big cities or limited spaces. High-density farming systems plus upward building can take advantage of already built-up areas and raise crop production.
Reduced Environmental Impact
By maximizing water efficiency, using fewer chemicals, and producing less waste, aquaponics has a lessened ecological footprint than traditional crop production practices. They are accountable for the environmental sustainability of agricultural practices, the production of healthy food, and the preservation of natural resources.
Conclusion
Being a householder of aquaponics, it is environment-friendly, resource-conserving, and can be practiced anywhere with little hassle. Through the practical implementation of the simple principles and the additional information provided in this comprehensive article. You can successfully design and construct your aquaponic system and gain access to healthy and tasty meals. Happy aquaponics!
FAQs
What is aquaponics, and how does it work?
Ans:Aquaponics, generally speaking, is a system that combines aquaculture, or fish farming, with hydroponics, the method of growing plants in water. The aquaponics method of agriculture is sustainable since it combines aquaculture and hydroponics. In the aquaponics system, the waste from fish provides plants with a source of nutrients, which clean and filter the water for the fish. The beneficial bacteria convert fish waste into nutrients that plants can absorb, and the nutrient-rich end product makes a perfect compost and fertilizer.
Describe the main parts of a hydroponic system.
Ans: The main elements are the fish tank for aquaculture, growing beds filled with a nutrient-rich medium for plants, a water pump to circulate water within the fish tank, and growing beds topped with a piping system for water flow. Hence, the correctness of design and layout is an indispensable part of any system.
What are the types of aquaponics systems available?
Ans: Aquaponics systems can be categorized into three main types: Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Media Bed, and Deep Water Culture (DWC). Every system differs in how it distributes water between the fish tank and the plant bed, meeting different types of plants and their specific growth requirements.
What must be considered when planning and constructing aquaponics systems?
Ans: Some factors must be taken into account, including the number of space required, the desired crops to be planted, the system complexity, the budget, and the reason why the system should be implemented. It’s imperative to choose the suitable fish and plants that can cohabitate, the right materials and equipment and set up the system accurately to allow efficient water flow and the best conditions for growth.
Why aquaponics?
Ans: Aquaponics offers multiple advantages, such as resource efficiency accomplished through water and nutrient reuse, the use of the space in different ways in various environments, and lessened environmental impact in comparison with traditional farming methods. Moreover, aquaponics helps increase health by providing access to fresh and nutritious foods while encouraging sustainability and conservation of natural resources.